Bearings are available with different types of shields and seals, commonly referred to as closures. These closures are not always essential; however shielded and sealed bearings provide much better protection from contamination and help retain the bearing lubricant.
Shields (ZZ)
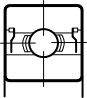 Most of our bearings are available with metal shields. Shields are designed to prevent larger particles from entering the bearing and also to keep grease inside the bearing. They may be pressed into the bearing’s outer ring (non-removable) or retained by a circlip (removable). As the shields make no contact with the inner ring, they do not increase starting or running torque. Shields on stainless steel bearings are generally made from AISI 304 stainless steel.
Most of our bearings are available with metal shields. Shields are designed to prevent larger particles from entering the bearing and also to keep grease inside the bearing. They may be pressed into the bearing’s outer ring (non-removable) or retained by a circlip (removable). As the shields make no contact with the inner ring, they do not increase starting or running torque. Shields on stainless steel bearings are generally made from AISI 304 stainless steel.
- Prevent contamination by larger particles
- Reduce lubricant leakage
- Do not increase torque
- Wide temperature range, especially stainless steel
Contact Seals (2RS)
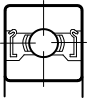
 The standard bearing seal consists of nitrile/BUNA-N rubber bonded to a metal washer. The washer is made of SPCC cold rolled steel for chrome steel bearings or 304 stainless steel for stainless steel bearings. High temperature PTFE (Teflon) seals or Viton seals are available on some sizes. The inner lip of the seal rubs against the bearing inner ring to provide an effective seal against smaller particles such as dust and moisture while preventing lubricant leakage. Contact seals produce much higher frictional torque levels than shields and reduce the maximum speed of a bearing. Below -40°C nitrile rubber and viton will stiffen and provide a less effective seal so PTFE seals or metal shields should be considered for very low temperatures.
The standard bearing seal consists of nitrile/BUNA-N rubber bonded to a metal washer. The washer is made of SPCC cold rolled steel for chrome steel bearings or 304 stainless steel for stainless steel bearings. High temperature PTFE (Teflon) seals or Viton seals are available on some sizes. The inner lip of the seal rubs against the bearing inner ring to provide an effective seal against smaller particles such as dust and moisture while preventing lubricant leakage. Contact seals produce much higher frictional torque levels than shields and reduce the maximum speed of a bearing. Below -40°C nitrile rubber and viton will stiffen and provide a less effective seal so PTFE seals or metal shields should be considered for very low temperatures.
- Good protection against contamination
- Greatly reduce lubricant leakage
- Reduce maximum speed by approx. 40%
- Greatly increase bearing torque
- Temp. range –40°C/+110°C for nitrile rubber
- Temp. range –40°C/+230°C for Viton
- Temp. range –100°C/+260°C for glass fibre re-inforced PTFE
Non-Contact Seals (2RU)
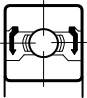 These seals are also made of nitrile rubber bonded to a metal washer but do not rub against the bearing inner ring and therefore do not have the same effect on bearing torque and maximum speed as contact seals so can be used for low torque, high speed applications. They offer superior protection over metal shields but do not provide as effective a seal as the contact type. Some bearing types are available with PE, PEEK or PTFE non-contact seals for temperature extremes or increased corrosion resistance.
These seals are also made of nitrile rubber bonded to a metal washer but do not rub against the bearing inner ring and therefore do not have the same effect on bearing torque and maximum speed as contact seals so can be used for low torque, high speed applications. They offer superior protection over metal shields but do not provide as effective a seal as the contact type. Some bearing types are available with PE, PEEK or PTFE non-contact seals for temperature extremes or increased corrosion resistance.
- Good protection against contamination
- Reduced lubricant leakage
- No torque increase
- Do not affect maximum speed
- Temp. range –40°C/+110°C for nitrile rubber
- Temp. range –40°C/+80°C for PE
- Temp. range –70°C/+250°C for PEEK
- Temp. range –190°C/+220°C for PTFE
Do you require high contamination protection?
For applications in the food and beverage or pharmaceutical industry, equipment must adhere to strict hygiene and safety standards. In these environments, contamination protection is of utmost importance, so opting for a contact seal is favourable to ensure dust does not enter the bearing. For equipment that deals with regular wash-downs, a contact seal will also offer effective water resistance. This will stop grease washing out of the bearing, the roller or balls skidding or the creation of excess heat. Many steel bearings for this industry need to be supplied with non-toxic lubricants approved to NSF (formerly USDA) H1 or H2 standards.
Will the bearing be operating in extreme temperature conditions?
Shielded metal bearings can generally withstand higher temperatures than sealed bearings. For high temperature applications 440 grade stainless steel bearings can be used at temperatures of up to 300°C. Rubber or plastic may risk melting if subjected to extreme conditions and can cause the bearing to fail if pieces melt off and enter the raceway. In these scenarios, a shielded bearing is advisable.
What speed will the bearing be operating at?
For high speed applications such as cycling and skateboarding, a non-contact seal is a preferable option. Offering greater contamination protection than shields, non-contact seals do not affect maximum speed or bearing torque.
